Thales of Miletus Discovered Static Electricity
Thales of Miletus was a pre-Socratic Greek thinker, scientist, and urologist from Miletus in peninsula (present-day Milet in Turkey). Thales is recognized for breaking from the use of mythology to explain the world and the universe, and instead of explaining natural objects and phenomena by theories and hypotheses, in a precursor to modern science.

In arithmetic, Thales used geometry to calculate the heights of pyramids and the distance of ships from the shore. He is the primary identified individual to use logical thinking applied to pure mathematics, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' theorem. He is the primary identified individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed.
Thales of Miletus created a series of observations on electricity around 600 BCE, from which he believed that friction rendered amber magnetic, in contrast to minerals such as magnetite, which needed no rubbing. Thales was incorrect in basic cognitive process the attraction was thanks to a magnetic impact, but later science would prove a link between magnetism and electricity.
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within the surface or on the surface of a material. The charge remains untilit is able to move away by suggests that of an electrical current or discharge. Static electricity is known as in distinction with electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.
A static charge is created whenever 2 surfaces contact and separate, and a minimum of one amongst the surfaces contains a high resistance to current (and is, therefore, an electrical insulator).
In 1600, William Gilbert coined the word “Electricus”. Later in 1752, this was termed as “Electricity” by Benjamin Franklin.
Stephen Gray Discovered Insulator and Conductor

Stephen grey (December 1666 – seven Feb 1736) was Associate in Nursing English skilled worker and physicist World Health Organization was the first to consistently experiment with conductivity. He additionally 1st created the excellence between physical phenomenon and insulation, and discovered the action-at-a-distance development of static induction.
An electrical dielectric could be a material whose internal electric charges don't flow freely. It means under the influence of an electric field, very little electric current will flow through it.
Insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. Conductors can conduct electric current more easily.
Benjamin Franklin Discovered Lightning is Electrical

Benjamin Franklin (January 17, 1706 – April 17, 1790) was AN American learned person. He was a serious figure within the American Enlightenment and therefore the history of physics for his discoveries and theories relating to electricity.
Franklin designed a "dissectible" capacitor thatwas wide employed in demonstrations. The jar is made out of a glass cup nested between 2 fairly snugly fitting metal cups. When the jar is charged with a high voltage and thoroughly razed, it's discovered that everyone the components is also freely handled while not discharging the jar. If the pieces are re-assembled, a large spark may still be obtained from it.
Franklin's electrical experiments light-emitting diode to his invention of the lightning rod. He aforementioned that conductors with a {pointy} instead of a sleek point might discharge wordlessly, and at a far greater distance. He deduced that this could help protect buildings from lightning by attaching "upright Rods of Iron, made sharp as a Needle and gilt to prevent Rusting, and from the Foot of these Rods a Wire down the surface of the Building into the bottom
Ewald Georg Von Kleist and Pieter Van Musschenbroek Invented Leyden Jars

A Leiden jar could be a device that "stores" electricity between two electrodes on the within and outdoors of a glass jar.
A Leiden jar consists of a glass jar with metal foil. This metal foil is cemented to the inside and the outside surfaces of glass jar.
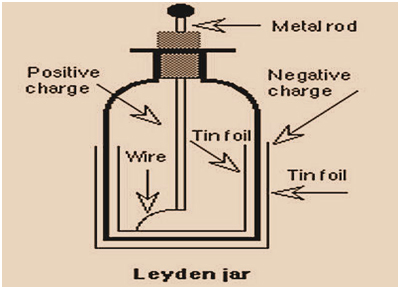
A metal terminal sticking vertically through the jar lid to create contact with the inner foil. It was the original form of a capacitor (it is originally known as a "condenser")
Charles Augustin De Coulomb Formulated Coulomb’s Law
Charles-Augustin Delaware Coulomb (14 June 1736 – 23 August 1806) was a French applied scientist and scientist. He is known for developing Coulomb's law, the description of the electrostatic force of attraction and repulsion. The SI unit of electric charge, the coulomb, was named in his honor in 1908.

Coulomb's law, or Coulomb's inverse-square law, is a law of physics that describes force interacting between static electrically charged particles. The force of interaction between the fees is enticing if the fees have opposite signs (i.e., F is negative) and repulsive if like-signed (i.e., F is positive).
Andre Marie Ampere Published His Law Of “Electrodynamics”
Called as “Ampere’s Law”

Andre-Marie Ampere (20 January 1775 – ten Gregorian calendar month 1836) was a French scientist and man of science WHO was one in every of the founders of the science of classical electromagnetism, that he referred to as "electrodynamics".
Ampre also provided a physical understanding of the electromagnetic relationship, theorizing the existence of an "electrodynamic molecule" (the forerunner of the idea of the electron) that served as the component element of both electricity and magnetism.
In classical electromagnetism, Ampere's circuital law relates the integrated magnetic field around a closed loop to the electric current passing through the loop. James Clerk Maxwell (not Ampere) derived it mistreatment hydrokinetics in his 1861 paper "On Physical Lines of Force" and it's currently one in every of the Maxwell equations, which form the basis of classical electromagnetism.
GEORG OHM INTRODUCED THE CONCEPT OF ELECTRICALRESISTANCE

The resistivity of electrical|an electrical}al conductor may be a live of the problem to pass associate degree electric current through that conductor. The SI unit of resistivity is that the ohm (Ω), whereas electrical electrical phenomenon is measured in siemens (S).
The inverse amount is electrical electrical phenomenon, and is that the ease with that an electrical current passes
Georg Ohm Introduced Ohm’s Law
Georg Simon Ohm (16 March 1789 – half-dozen Gregorian calendar month 1854) was a German man of science and man of science. Ohm began his analysis with the new chemistry cell, unreal by Italian soul Alessandro Conte Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasia Volta. Using instrumentality of his own creation, Ohm found that there's an instantaneous proportion between the potential variations (voltage) applied across a conductor and therefore the resultant current.

Ohm's law states that this through a conductor between 2 points is directly proportional to the voltage across the 2 points. Introducing the constant of proportion, the resistance, one arrives at the standard mathematical equation that describes this relationship:
I=V/R
Where,
I is that the current through the conductor in units of amperes
V is that the voltage measured across the conductor in units of volts
R is that the resistance of the conductor in units of ohms
More specifically, law states that the R during this relation is constant.
Hans Christian Orsted Discovered Magnetic Field.

Hans Christian Orsted (14 August 1777 – 9 March 1851) was a Danish physicist and chemist who discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields. After his research, the connection found between electricity and magnetism. Oersted's law named after him.
On 21 April 1820, during a lecture, Orsted noticed a compass needle deflected from magnetic north when an electric current from a battery was switched on and off, confirming a direct relationship between electricity and magnetism. A magnetic field is a force field that is created by moving electric charges (electric currents) and magnetic dipoles and exerts a force on other nearby moving charges and magnetic dipoles. At any given purpose, it has a direction and a magnitude (or strength), so it is represented by a vector field.
 The term is employed for 2 distinct however closely connected fields denoted by the symbols B and H, where, within the International System of Units of Units, H is estimated in units of amperes per meter and B is estimated in Teslas or Newtons per meter per ampere.
The term is employed for 2 distinct however closely connected fields denoted by the symbols B and H, where, within the International System of Units of Units, H is estimated in units of amperes per meter and B is estimated in Teslas or Newtons per meter per ampere.
Magnetic fields may be made by moving electrical charges and therefore the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles related to an elementary quantum property, their spin. Magnetic fields and electrical fields are reticulate and are each part of the magnetism force, one amongst the four elementary forces of nature.
Michael Faraday Published The Law Of Induction

Michael Faraday FRS (22 Sep 1791 – 25 August 1867) was a British human United Nations agency contributed to the study of electromagnetism and chemistry. His main discoveries embody the principles underlying magnetism induction, magnetism and electrolysis.
Faraday's law of induction could be a basic law of electromagnetism predicting however a magnetic flux can move with an electrical circuit to provide AN voltage} (EMF)—a phenomenon known as magnetism induction. It is the elemental operational principle of transformers, inductors, and many kinds of electrical motors, generators and solenoids.
Michael Faraday Invented Transformer
Michael Faraday FRS (22 Gregorian calendar month 1791 – 25 August 1867) was a British human World Health Organization contributed to the study of electromagnetism and chemistry. His main discoveries embrace the principles underlying magnetic attraction induction, magnetic attraction and electrolysis.
An electrical device is associate device that transfers current between 2 or a lot of circuits through magnetic attraction induction.
A varied current in one coil of the electrical device produces a varied force field, that successively induces a varied electrical phenomenon (emf) or "voltage" in a very second coil.
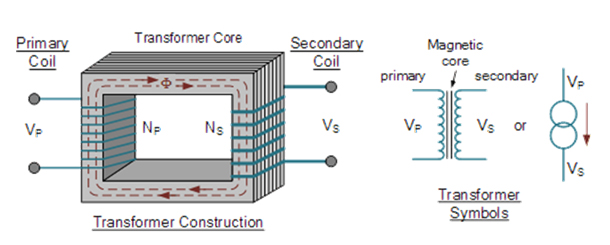 Power will be transferred between the two coils through the force field, while not a gold association between the 2 circuits. Faraday's law of induction discovered in 1831 delineated this impact. Transformers are wont to increase or decrease the alternating voltages in power applications.
Power will be transferred between the two coils through the force field, while not a gold association between the 2 circuits. Faraday's law of induction discovered in 1831 delineated this impact. Transformers are wont to increase or decrease the alternating voltages in power applications.
Since the invention of the primary constant-potential electrical device in 1885, transformers became essential for the transmission, distribution, and utilization of electricity power. A wide vary of electrical device styles is encountered in electronic and electrical power applications. Transformers point size from RF transformers but a metric capacity unit in volume to units interconnecting the ability grid deliberation many tons.
Samuel Morse Developed Telegraphy And The Morse Code

Telegraphy is that the long-distance transmission of matter or symbolic (as against verbal or audio) messages while not the physical exchange of Associate in Nursing object bearing the message. Semaphore is a method of telegraphy.
Telegraphy needs that the tactic used for cryptography the message be identified to each sender and receiver. Many methods are designed according to the limits of the signaling medium used. The use of smoke signals, beacons, mirrored lightweight signals, and flag semaphore signals are early examples.
 In the nineteenth century, the harnessing of electricity led to the invention of electrical telegraphy. The advent of radio within the early twentieth century led to radiotelegraphy and different varieties of wireless telegraphy.
In the nineteenth century, the harnessing of electricity led to the invention of electrical telegraphy. The advent of radio within the early twentieth century led to radiotelegraphy and different varieties of wireless telegraphy.
In the net age, telegraphic suggests that developed greatly in sophistication and easy use, with language interfaces that hide the underlying code, permitting such technologies as electronic message and instant messaging.
At present, the Morse codes are used in HAM Radio or Amateur Radio communication system.
GUGLIELMO MARCONI MADE FIRST TRANSATLANTIC RADIO BROADCAST

Guglielmo Marconi (25 Apr 1874 – 20 July 1937) was Associate in Nursing Italian discoverer and technologist famous for his pioneering work on long-distance radio transmission. He is also known for his development of Marconi's law and a radiotelegraph system.
He is attributable because the discoverer of radio and he shared the 1909 Nobel prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand Braun "in recognition of their contributions to the event of Wireless Telegraphy".
At the flip of the twentieth century, Guglielmo Marconi began investigation the means that to signal utterly across the Atlantic so as to contend with the transatlantic telegraph cables. Marconi established a wireless transmittal station at {marconi|Marconi|GuglielmoMarconi electrical engineer} House, Rosslare Strand, Co. Wexford in 1901 to act as a link between Poldhu in county, England and Clifden in Co. Galway, Ireland.
Marconi was additionally associate in Nursing bourgeois, businessperson, and founder of The Wireless Telegraph & Signal Company in the United Kingdom in 1897.
GUGLIELMO MARCONI MADE FIRST TRANSATLANTIC RADIO BROADCAST

Alexander Graham Bell (3 March, 1847 – 2, August 1922) was a someone, inventor, engineer, and conceiver. He is credited with inventing and patenting the first practical telephone. He additionally based the Yankeephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1885.
 His analysis on hearing and speech additional semiconductor diode him to experiment with hearing devices that eventually culminated in Bell being awarded the primary U.S. patent for the telephone in 1876.
His analysis on hearing and speech additional semiconductor diode him to experiment with hearing devices that eventually culminated in Bell being awarded the primary U.S. patent for the telephone in 1876.
JOHN AMBROSE FLEMING INVENTED DIODE

Sir John Ambrose Fleming (29 November 1849 –
18 Gregorian calendar month 1945),
AN English applied scientist and man of science,
invented the first thermionic valve or vacuum tube, also
designed the transmitter with that the primary transatlantic
radio transmission was made, and also established the
left-hand rule for electric motors..
 A diode could be a two-terminal electronic part that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it is low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A vacuum tube diode utilizes thermionic emission of electrons and unidirectional conduction between the cathode and plate.
A diode could be a two-terminal electronic part that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it is low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A vacuum tube diode utilizes thermionic emission of electrons and unidirectional conduction between the cathode and plate.
A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices.
The discovery of uneven conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was created by German man of science Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes area unit product of chemical element, however alternative materials like metallic element compound and semiconductor area unit used.
JAlessandro Volta Invented Battery (Dry Cell).

After development of wet zinc-carbon batteries by Georges Leclanché in 1866, a German scientist Carl Gassner invented dry cell in 1886. A dry cell is a type of battery that is commonly used for portable electrical devices.
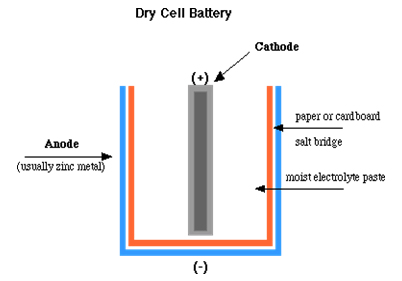 A Leclanche cell uses a paste solution, with merely enough wet to permit current to flow. Unlike a wet cell, a dry cell can operate in any orientation without spilling, as it contains no free liquid, making it suitable for portable equipment like calculators and mobile phones
A Leclanche cell uses a paste solution, with merely enough wet to permit current to flow. Unlike a wet cell, a dry cell can operate in any orientation without spilling, as it contains no free liquid, making it suitable for portable equipment like calculators and mobile phones
TELEVISION BROADCAST

John Logie Baird was a Scottish engineer, innovator, one in all the inventors of the mechanical tv, demonstrating the primary operating telecommunication system on twenty six Jan 1926, and creator of each the first publically incontestablecolor television system, and therefore the 1st strictly electronic color television kinescope.
In 1927, Baird transmitted a sign over 438 miles (705 km) of phone line between London and metropolis. In 1928, Baird's company (Baird tv Development Company/Cinema Television) broadcast the primary transatlantic tv signal, between London and ny, and therefore the 1st shore-to-ship transmission.
In 1928: General Electric establishes an experimental electro-mechanical television station in Schenectady, NY. In 1929, he became concerned within the 1st experimental mechanical tv service in Federal Republic of Germany. The station broadcasts a moving image from a "camera" using a Nikodisk with a 24-line resolution.
LEE DE FOREST INVENTED TRIODE

Lee de Forest (26, August 1873 – 30, June 1961) was an American inventor, self-described "Father of Radio", and a pioneer in the development of sound-on-film recording used for motion pictures. He had over 180 patents.
His most noted invention, in 1906, was the three-element "Audion" (triode) electron tube, the primary sensible amplification device. Although DeForest had only a limited understanding of how it worked, it was the foundation of the field of electronics, making possible radio broadcasting, long-distance telephone lines, and talking motion pictures, among countless other applications.
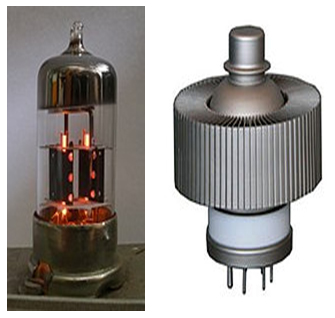 A tube is Associate in Nursing electronic amplifying electron tube consisting of 3 electrodes within Associate in Nursing exhausted glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode).
A tube is Associate in Nursing electronic amplifying electron tube consisting of 3 electrodes within Associate in Nursing exhausted glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode).
Developed from Lee Delaware Forest's 1906 Audion a partial electron tube that accessorial a grid conductor to the particle diode (Fleming valve), the tube was the primary sensible electronic electronic equipment and the relation of alternative varieties of vacuum tubes like the thermionic vacuum tube and thermionic valve.
Triodes were wide utilized in physical science devices like radios and televisions till the Nineteen Seventies, once transistors replaced them. Today, their main remaining use is in high-voltage RF amplifiers in radio transmitters and industrial RF heating devices. In recent years, there has been resurgence in demand for low power triodes due to renewed interest in tube-type audio systems by audiophiles who prefer the sound of tube-based electronics
KONRAD ZUSE DEVELOPED THE FIRST PROGRAMMABLE COMPUTER

Konrad Zuse (22 June 1910 – 18 December 1995) was a German technologist, inventor, and pc pioneer. His greatest accomplishment was the world's initial programmable computer; the purposeful program-controlled Turing-complete Z3 became operational in might 1941. Zusehas typically been thought to be the creator of the fashionable pc.
Zusewas additionally noted for the S2 electronic computer, considered the first process control computer. He based one amongst the earliest pc businesses in 1941, producing the Z4, which became the world's first commercial computer. From 1943 to 1945 he designed the first high-level programming language, Plankalkul in 1969.
In 1936, Konrad Zuse anticipated in two patent applications that machine directions could be keep within the same storage used for information. The University of Manchester's Baby is generally recognized as the world's first electronic computer that ran a stored program—an event that occurred on 21 June 1948.
However, the Baby was not thought to be a full-fledged pc, but more a proof of concept predecessor to the Manchester Mark 1 computer, which was first put to research work in April 1949.
On vi might 1949, the EDSAC in Cambridge ran its first program, making it arguably "the first complete and fully operational regular electronic digital stored-program computer".
It is typically claimed that the IBM SSEC, operational in January 1948, was the primary stored-program computer; this claim is disputed, not least as a result of the stratified memory system of the SEC, and because some aspects of its operations, like access to relays or tape drives, were determined by plugging.
The first stored-program computer to be built in continental Europe was the MSM, completed in the Soviet Union in 1951.
EDWIN HOWARD ARMSTRONG DEVELOPED ELECTRONIC OSCILLATOR

Edwin Howard Armstrong (December eighteen, 1890 – Gregorian calendar month thirty one, 1954) was associate Yankee engineer and discoverer, best better known for developing FM (frequency modulation) radio and the radio receiver system. He command forty-two patents and received varied awards, together with the primary ribbon of Honor awarded by the Institute of Radio Engineers (now IEEE).
An electronic generator is associate electronic circuit that produces a periodic, periodical sign, usually a wave or a sq. wave.
 They are widely used in many electronic devices. Common samples of signals generated by oscillators embrace signals broadcast by radio and tv transmitters, clock signals that regulate computers and quartz clocks, and also the sounds made by electronic beepers and video games.
They are widely used in many electronic devices. Common samples of signals generated by oscillators embrace signals broadcast by radio and tv transmitters, clock signals that regulate computers and quartz clocks, and also the sounds made by electronic beepers and video games.
Oscillators are usually characterized by the frequency of their output signal:
• A low-frequency oscillator (LFO) is an electronic oscillator that generates a frequency below approximately 20 Hz. This term is usually utilized in the sphere of audio synthesizers, to tell apart it from associate degree frequency generator.
• An audio oscillator produces frequencies in the audio range, about 16 Hz to 20 kHz.
• An RF oscillator produces signals in the radio frequency (RF) range of about 100 kHz to
Oscillators designed to provide a dynamic AC output from a DC supply are typically referred to as inverters.